1.2 Overview of the course modules
Free PreviewThe course is divided into 8 modules:
- Module 1 – Introduction to CarbonLite Retrofit
- Module 2 – Climate and weather
- Module 3 – UK construction
- Module 4 – Heat and energy targets
- Module 5 – Moisture and air quality
- Module 6 – Case studies
- Module 7 – Building services
- Module 8 – Financial rationale
Note: All images below are discussed (and magnified) in the relevant module. Here, they are just for illustration.
Module 1 – Introduction to CarbonLite Retrofit
As already stated, this module provides an overview to each module and goes on to outline the benefits of achieving robust low energy retrofit.
Module 2 – Climate and weather
Climate is what you expect. Weather is what you get.

This module looks at the way our climate affects our buildings.
It considers this on different scales:
- global
- national
- regional
- site
- building
- microclimates within the building and its fabric
The implications of sun, wind, rain and flooding are summarised.
This module also looks into the future and considers how climate change will modify the climates that we experience now.
Module 3 – UK construction

This module starts with a summary of changes to typical UK construction over the last 150 years.
It has a lesson on typical traditional construction and another on non-traditional UK construction.
Examples of as built and retrofitted non-traditional buildings are given.
Even within “standard construction”, there is considerable regional variation in wall and floor characteristics – examples are given to illustrate these.
Finally, the effect of existing defects (sometimes as a result of previous “improvements”) is discussed. Understanding these defects is critical to selecting a suitable retrofit strategy.
Module 4 – Heat and energy targets
This module covers:

- the basic physics of energy, power and the transfer of energy.
- annual energy consumption and how heat load is calculated.
- useful, delivered and primary energy
- energy performance and heat loss
- 5 key factors of thermal performance (in new build and retrofit)
- embodied energy in retrofit (the carbon ‘burp’)
- compares the 3 most common categories of houses
- uses these examples to look at form factor, heat loss, thermal bridges
- heat demand targets proposed for CLR Certification
Module 5 – Moisture and air quality
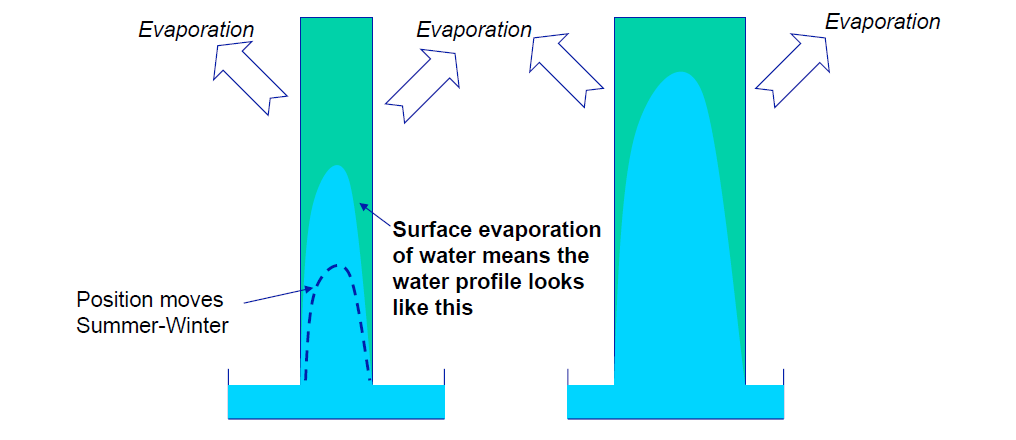
This module considers:
- biological decay,
- where moisture in our homes comes from.
- how it exists in the building
- how it moves around / in / out of the building
- damage caused by salts in buildings
- wetting and drying in buildings

Processes such as evaporation, condensation, diffusion and capillary action are explained.
Problems and solutions are considered, along with heat sources and their effect on the different microclimates within a building. There are examples showing cases where issues have developed.
Hygrothermal modelling and monitoring is also covered.
Module 6 – Case studies
Case studies are being added to this module over time. Examples include the following range of scenarios:

- solid brick walls with internal insulation
- solid brick walls with external insulation (permeable)
- solid brick walls with external insulation (semi-permeable)
- a loft space with condensation issues
- a misdiagnosed cavity wall, internally insulated
- a listed building with wood fibre internal insulation
- a barn conversion with timber frame internal wall insulation and ventilated cavity
Moisture monitoring in each case has been carried out and the results explained as part of the case study.
Module 7 – Building services

This module covers fuels and systems for heating and hot water (i.e. gas, oil, LPG, electricity and biomass with traditional and modern types of boilers)
It describes a range of ventilation systems including mechanical ventilation and heat recovery (MVHR) and mechanical extract ventilation (MEV) as well as other options.
It talks briefly about lighting and appliances, and renewable technologies.
Module 8 – Financial rationale
This module considers the benefits of retrofitting and the disadvantages associated with “doing nothing” to a building.
It looks at the existing condition of the UK housing stock and the way that home owners, landlords and government make decisions around home modifications.
Several methods for assessing or making a business case for retrofit are explained and compared (pay back period, discounted cash flow method, etc).
Extensive financial modelling of different types of house with different efficiency measures has been carried out.
Outcomes for light, medium and deep retrofit are given for the 3 most common UK house types and a selection of scenarios are illustrated.
Carbon mitigation costs, health costs and false economies are considered.
CLR students are all encouraged to join the AECB webinars, many of which focus on aspects of building retrofit. These webinars are free and give the opportunity to learn from and put questions to leading experts.
Click here to see the latest webinars in the series.