1.1 Introduction to CarbonLite Retrofit
Free PreviewContributors to Module 1
Andy Simmonds, Eric Parkes,
How can we best maintain, repair and improve our buildings?
What kind of retrofit will work out best in the long term?
What are the potential pitfalls and false economies to avoid?
The aim of this course
…is to enable retrofitters to achieve improved buildings that enjoy:
- A future-proofed increase in winter and summer internal comfort levels
- Excellent indoor air quality
- Low running costs with a minimal energy performance gap
- Retrofit strategies that are ‘economically optimised’ for owners and occupants
- CO2 savings at low to negative cost per tonne of CO2 saved
- Avoidance or reduction of risks from unintended consequences related to moisture
The key objectives of Module 1 are:
- to introduce the topic of robust, low energy retrofit
- to provide an overview of each Module within this course
- to outline the benefits of achieving a robust low energy retrofit
Module 1 consists of the following lessons:
Lesson 1 – Introduction to CarbonLite Retrofit
Lesson 2 – Overview of the course modules
Lesson 3 – Benefits of a successful retrofit
Lesson 4 – Comfort and health
Lesson 5 – Ventilation and air quality
Lesson 6 – National and international context
Introduction to robust, low energy retrofit
This course considers the following themes:
- Why aim for robust low energy retrofit? (The benefits we want to achieve, the pitfalls we want to avoid.)
- How can this kind of retrofit be achieved?
- What do I need to understand to reduce or avoid risks to occupant and building health?
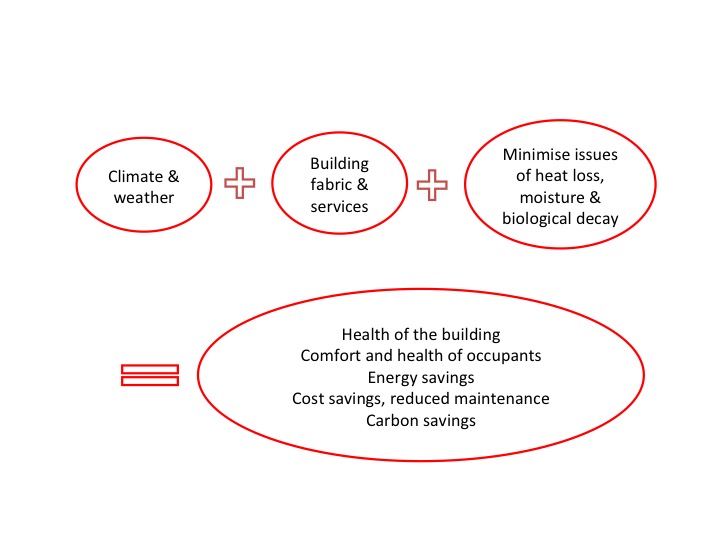
Central to a successful retrofit are three key principles:
- Heating energy should be used much more efficiently while at the same time
- Comfort should increase, and
- Health of occupants and of building fabric should be protected and enhanced.
The diagram below sums up these key principles.
Some useful definitions
Improve: to make or become better
Repair: to put something that is damaged, broken, or not working correctly, back into good condition or make it work again.
Renovate: to repair and improve something, especially a building.
Refurbish: to make a building look new again by doing work such as painting, repairing, and cleaning.
Retrofit: to add (a component or accessory) to something that did not have it when manufactured (or built).
We will also use the following terms:
- light retrofit (= shallow retrofit)
- medium retrofit
- deep retrofit
Whole House retrofit or refurbishment can be carried out
- in one go, or
- as a series of carefully phased steps to achieve the same end result.
The starting point should always be a comprehensive whole house retrofit plan (e.g. the Overall Retrofit Plan proposed by the Passivhaus Institute for stepwise retrofit with Passive House components): http://europhit.eu/certification-retrofit-plans